WELDING INSPECTION TECHNOLOGY WORKBOOK - MODULE 3
VT Test - MODULE 3
Q3-1 Which of the following is a function of the flux coating of a SMAW electrode?
a. insulating
b. alloying
c. deoxidation
d. shielding
e. all of the above
Q3-2 In the AWS system of SMAW electrode designations, the next to the last digit refers to:
a. impact strength
b. electrode coating
c. welding position
d. strength
e. none of the above
Q3-3 Which of the following is an incorrect statement about a SMAW electrode designated as E7024?
a. It is a low hydrogen type.
b. The weld deposit has a minimum tensile strength of 70,000 psi.
c. It is suitable for use in the flat and horizontal fillet positions only.
d. It is an electrode for welding carbon steel.
e. none of the above
Q3-4 Of the following which is not an essential part of a typical SMAW system?
a. constant current power supply
b. wire feeder
c. covered electrode
d. electrode lead
e. work lead
Q3-5 Which of the following welding problems is the result of a distorted magnetic field that deflects
the welding arc?
a. cracks
b. short circuiting
c. arc blow
d. insufficient welding current
e. all of the above
Q3-6 Which of the following is not considered a type of metal transfer for GMAW?
a. short circuiting
b. spray
c. globular
d. droplet
e. pulsed arc
Q3-7 Which of the following types of metal transfer in GMAW provides the lowest amount of heat to
the workpiece, and therefore is prone to incomplete fusion?
a. short circuiting
b. spray
c. globular
d. droplet
e. pulsed arc
Q3-8 Which of the following gases can be used as shielding gases for GMAW?
a. carbon dioxide
b. argon-oxygen
c. argon-carbon dioxide
d. argon
e. all of the above
Q3-9 What type of welding process is pictured below?
a. SMAW
b. GMAW
c. FCAW
d. SAW
e. ESW
Q3-11 In the electrode designation system for FCAW, the second digit (1) in an electrode marked
(E71T-5) refers to:
a. strength
b. welding position
c. chemical composition
d. usability
e. none of the above
Q3-12 Which of the following is not always an essential element of an FCAW system?
a. constant voltage power supply
b. tubular electrode
c. wire feeder
d. external shielding gas
e. work lead
Q3-13 What aspect of the GTAW and PAW processes makes them different from the other arc welding
processes?
a. nonconsumable electrode
b. power supply
c. shielding
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
Q3-14 Shielding for the GTAW and PAW processes is primarily accomplished through the use of:
a. granular flux
b. slag
c. inert gas
d. oxygen
e. none of the above
Q3-15 A green stripe on a tungsten electrode designates:
a. pure tungsten
b. 1 % thoriated tungsten
c. 2% thoriated tungsten
d. zirconiated tungsten
e. none of the above
Q3-16 When welding aluminum with the GTAW process, what type of welding current is most commonly
used?
a. DCEP
b. DCEN
c. AC
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
Q3-17 SAW and ESW processes are similar in that:
a. both are an arc welding process
b. both use shielding gases
c. both use a granular flux, which becomes molten
d. a and b above
e. a and c above
Q3-18 The diagram below depicts what welding process?
a. SMAW
b. ESW
c. FCAW
d. SAW
e. GMAW
Q3-19 Solidification cracking due to improper width-to-depth ratio of the weld bead is a serious
problem primarily with which welding process?
a. SMAW
b. OFC
c. SAW
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
(23-20 Which one of the following processes is typically used in the flat position unless special apparatus
is employed?
a. GMAW
b. SAW
c. FCAW
d. SMAW
e. GTAW
Q3-21 Which of the following are not common to both GTAW and PAW?
a. nonconsumable tungsten electrode
b. constricting orifice
c. shielding gas nozzle
d. externally applied filler metal
e. none of the above
Q3-22 What technique is employed with PAW to produce full penetration welds without edge preparation?
a. stringer beads
b. weave beads
c. keyhole
d. backstep
e. none of the above
Q3-23 What welding process produces welds in a single pass, with the progression uphill along the I
joint?
a. SAW
b. ESW
c. FCAW
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
Q3-24 Which of the following is not an advantage of the ESW process?
a. high deposition rate
b. ease of setup
c. capable of joining thick sections
d. no tendency for angular distortion
e. none of the above
Q3-25 Which welding process is considered to be a chemical welding process?
a. SMAW
b. ESW
c. SAW
d. OAW
e. none of the above
Q3-26 Which arc welding process provides a very efficient means of joining attachments to some planar
surfaces?
a. OAW
b. SW
c. GMAW
d. GTAW
e. SMAW
Q3-27 Brazing differs from welding in that:
a. no filler metal is used
b. an oxyfuel flame is used
c. the base metal is not melted
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
Q3-28 For satisfactory results, a braze joint should have:
a. clean joint surfaces
b. a small clearance between pieces to be joined
c. a large surface area for the joint area
d. heat source
e. all of the above
Q3-29 Which of the following is an advantage of brazing?
a. ease of joining thick sections
b. ability to join dissimilar metals
c. ability to join thin sections
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
Q3-30 Of the following metals, which cannot be efficiently cut using OFC?
a. high-carbon steel
b. low-carbon steel
c. medium-carbon steel
d. austenitic stainless steel
e. none of the above
Q3-31 Which of the following gases can be used to perform OFC?
a. methylacetylene - propadiene (MPS)
b. propane
c. acetylene
d. methane (natural gas)
e. all of the above
Q3-32 Which of the following cutting processes can cut any metal?
a. OFC
c. PAC
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
b. CAC-A
Q3-33 The width of a cut is referred to as the:
a. gap
b. dross
c. kerf
d. drag
e. none of the above
Q3-34 The SMAW power source can be:
a. DCEN
b. AC
c. DCEP
d. all of the above
e. a and c above
Q3-35 Of the following, which is a noncontact welding process, requires no electrodes, and is not influenced
by the presence of magnetic fields?
a. ESW
b. PAW
c. LBW
d. a and b above
e. none of the above
Q3-36 Which of the following uses a focused beam of electrons as a heat source for fusion welding?
a. EBW
b. ESW
c. EGW
d. a and c above
e. none of the above
Q3-1 Which of the following is a function of the flux coating of a SMAW electrode?
a. insulating
b. alloying
c. deoxidation
d. shielding
e. all of the above
Q3-2 In the AWS system of SMAW electrode designations, the next to the last digit refers to:
a. impact strength
b. electrode coating
c. welding position
d. strength
e. none of the above
Q3-3 Which of the following is an incorrect statement about a SMAW electrode designated as E7024?
a. It is a low hydrogen type.
b. The weld deposit has a minimum tensile strength of 70,000 psi.
c. It is suitable for use in the flat and horizontal fillet positions only.
d. It is an electrode for welding carbon steel.
e. none of the above
Q3-4 Of the following which is not an essential part of a typical SMAW system?
a. constant current power supply
b. wire feeder
c. covered electrode
d. electrode lead
e. work lead
Q3-5 Which of the following welding problems is the result of a distorted magnetic field that deflects
the welding arc?
a. cracks
b. short circuiting
c. arc blow
d. insufficient welding current
e. all of the above
Q3-6 Which of the following is not considered a type of metal transfer for GMAW?
a. short circuiting
b. spray
c. globular
d. droplet
e. pulsed arc
Q3-7 Which of the following types of metal transfer in GMAW provides the lowest amount of heat to
the workpiece, and therefore is prone to incomplete fusion?
a. short circuiting
b. spray
c. globular
d. droplet
e. pulsed arc
Q3-8 Which of the following gases can be used as shielding gases for GMAW?
a. carbon dioxide
b. argon-oxygen
c. argon-carbon dioxide
d. argon
e. all of the above
Q3-9 What type of welding process is pictured below?
a. SMAW
b. GMAW
c. FCAW
d. SAW
e. ESW
Q3-10 Which of the following is not considered an arc welding process?
a. SMAW
b. GMAW
c. FCAW
d. ESW
e. none of the above
Q3-11 In the electrode designation system for FCAW, the second digit (1) in an electrode marked
(E71T-5) refers to:
a. strength
b. welding position
c. chemical composition
d. usability
e. none of the above
Q3-12 Which of the following is not always an essential element of an FCAW system?
a. constant voltage power supply
b. tubular electrode
c. wire feeder
d. external shielding gas
e. work lead
Q3-13 What aspect of the GTAW and PAW processes makes them different from the other arc welding
processes?
a. nonconsumable electrode
b. power supply
c. shielding
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
Q3-14 Shielding for the GTAW and PAW processes is primarily accomplished through the use of:
a. granular flux
b. slag
c. inert gas
d. oxygen
e. none of the above
Q3-15 A green stripe on a tungsten electrode designates:
a. pure tungsten
b. 1 % thoriated tungsten
c. 2% thoriated tungsten
d. zirconiated tungsten
e. none of the above
Q3-16 When welding aluminum with the GTAW process, what type of welding current is most commonly
used?
a. DCEP
b. DCEN
c. AC
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
Q3-17 SAW and ESW processes are similar in that:
a. both are an arc welding process
b. both use shielding gases
c. both use a granular flux, which becomes molten
d. a and b above
e. a and c above
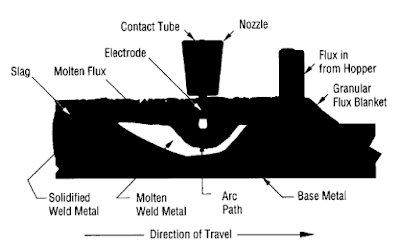
Q3-18 The diagram below depicts what welding process?
a. SMAW
b. ESW
c. FCAW
d. SAW
e. GMAW
Q3-19 Solidification cracking due to improper width-to-depth ratio of the weld bead is a serious
problem primarily with which welding process?
a. SMAW
b. OFC
c. SAW
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
(23-20 Which one of the following processes is typically used in the flat position unless special apparatus
is employed?
a. GMAW
b. SAW
c. FCAW
d. SMAW
e. GTAW
Q3-21 Which of the following are not common to both GTAW and PAW?
a. nonconsumable tungsten electrode
b. constricting orifice
c. shielding gas nozzle
d. externally applied filler metal
e. none of the above
Q3-22 What technique is employed with PAW to produce full penetration welds without edge preparation?
a. stringer beads
b. weave beads
c. keyhole
d. backstep
e. none of the above
Q3-23 What welding process produces welds in a single pass, with the progression uphill along the I
joint?
a. SAW
b. ESW
c. FCAW
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
Q3-24 Which of the following is not an advantage of the ESW process?
a. high deposition rate
b. ease of setup
c. capable of joining thick sections
d. no tendency for angular distortion
e. none of the above
Q3-25 Which welding process is considered to be a chemical welding process?
a. SMAW
b. ESW
c. SAW
d. OAW
e. none of the above
Q3-26 Which arc welding process provides a very efficient means of joining attachments to some planar
surfaces?
a. OAW
b. SW
c. GMAW
d. GTAW
e. SMAW
Q3-27 Brazing differs from welding in that:
a. no filler metal is used
b. an oxyfuel flame is used
c. the base metal is not melted
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
Q3-28 For satisfactory results, a braze joint should have:
a. clean joint surfaces
b. a small clearance between pieces to be joined
c. a large surface area for the joint area
d. heat source
e. all of the above
Q3-29 Which of the following is an advantage of brazing?
a. ease of joining thick sections
b. ability to join dissimilar metals
c. ability to join thin sections
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
Q3-30 Of the following metals, which cannot be efficiently cut using OFC?
a. high-carbon steel
b. low-carbon steel
c. medium-carbon steel
d. austenitic stainless steel
e. none of the above
Q3-31 Which of the following gases can be used to perform OFC?
a. methylacetylene - propadiene (MPS)
b. propane
c. acetylene
d. methane (natural gas)
e. all of the above
Q3-32 Which of the following cutting processes can cut any metal?
a. OFC
c. PAC
d. a and b above
e. b and c above
b. CAC-A
Q3-33 The width of a cut is referred to as the:
a. gap
b. dross
c. kerf
d. drag
e. none of the above
Q3-34 The SMAW power source can be:
a. DCEN
b. AC
c. DCEP
d. all of the above
e. a and c above
Q3-35 Of the following, which is a noncontact welding process, requires no electrodes, and is not influenced
by the presence of magnetic fields?
a. ESW
b. PAW
c. LBW
d. a and b above
e. none of the above
Q3-36 Which of the following uses a focused beam of electrons as a heat source for fusion welding?
a. EBW
b. ESW
c. EGW
d. a and c above
e. none of the above



Comments
Post a Comment